Top 5 Phlebotomy Techniques Every Healthcare Professional Should Master
Phlebotomy is a vital skill in healthcare, enabling the collection of blood samples for diagnostics, research, and treatment. Proficiency in key phlebotomy techniques ensures accurate results, minimizes patient discomfort, and maintains safety standards. Here are the top five techniques every healthcare professional must master:
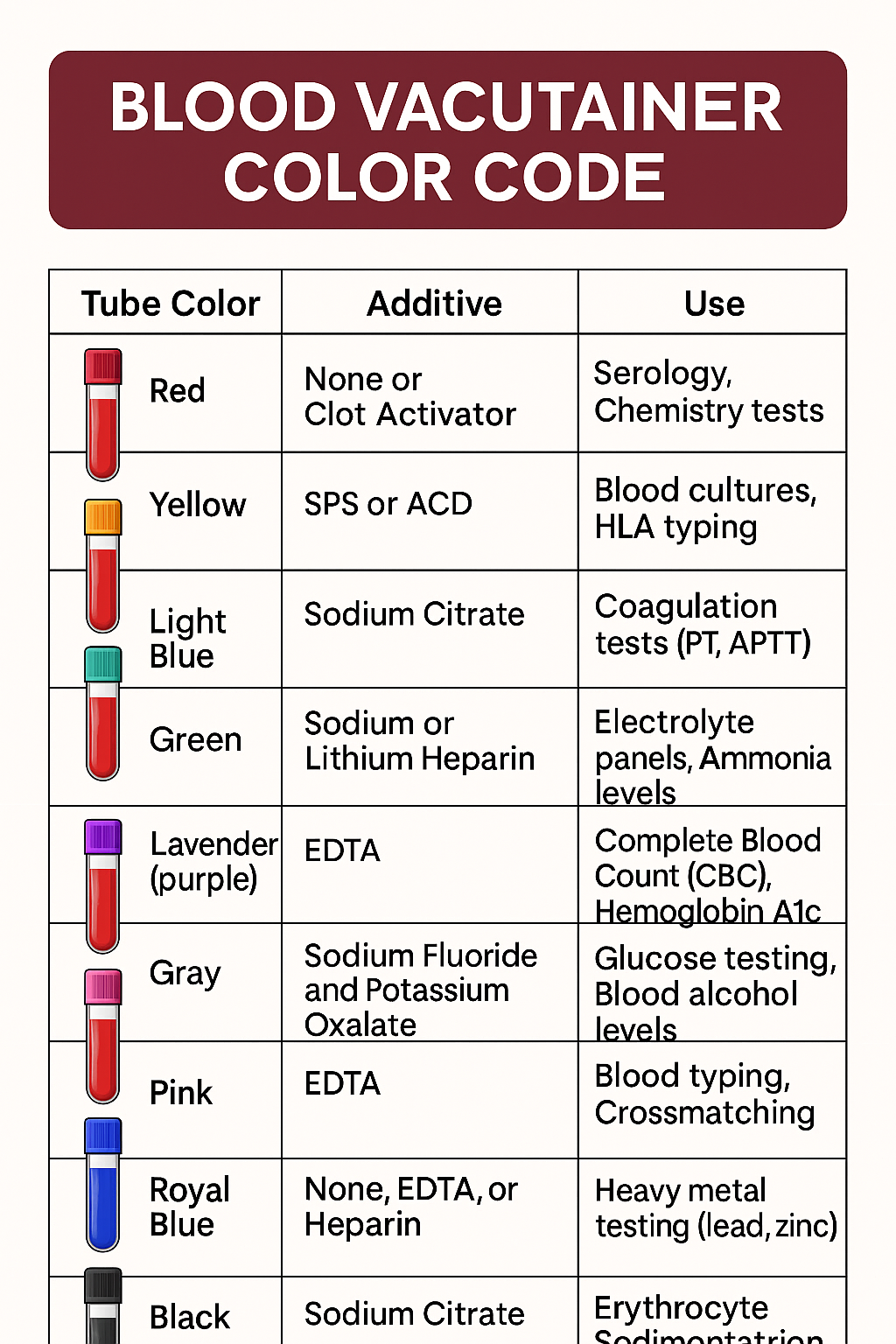
1. Venipuncture
Venipuncture is the cornerstone of phlebotomy and involves drawing blood from a vein, typically in the arm. Key steps include:
- Patient Identification and Preparation: Verify the patient’s identity and explain the procedure to ensure they are comfortable.
- Vein Selection: The median cubital vein is the most commonly used due to its accessibility and low risk of complications.
- Sterile Technique: Thoroughly clean the site to prevent infection.
- Proper Needle Angle: Insert the needle at a 15-30 degree angle to access the vein without causing unnecessary trauma.
- Order of Draw: Follow the correct sequence when using multiple collection tubes to avoid cross-contamination.
2. Capillary Puncture (Fingerstick or Heelstick)
Capillary puncture is ideal for collecting small blood samples, particularly in children or situations where venipuncture is difficult. This technique is commonly used for:
- Fingersticks: Performed on the middle or ring finger of adults and children.
- Heelsticks: Performed on the outer edges of an infant’s heel.
Best practices include:
- Site Warming: Warm the area to increase blood flow for easier collection.
- Correct Lancet Use: Use a lancet with the appropriate depth to avoid injury.
- Minimized Pressure: Avoid excessive squeezing, which can damage blood cells and compromise the sample.
3. Arterial Puncture
Arterial puncture is performed to collect arterial blood, primarily for analyzing oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH levels. This procedure is more invasive and requires advanced training. Essential steps include:
- Site Selection: The radial artery is the most commonly used, with the brachial and femoral arteries as alternatives.
- Allen Test: Conduct this test before puncturing the radial artery to confirm adequate collateral blood flow.
- Aseptic Technique: Use strict sterile practices to reduce the risk of infection.
- Firm Pressure Post-Procedure: Apply consistent pressure for at least 5-10 minutes to prevent bleeding or hematoma.
4. Blood Culture Collection
Blood culture collection is crucial for diagnosing infections. Proper technique reduces the risk of contamination and ensures accurate results. Key considerations include:
- Sterile Skin Preparation: Use antiseptics like chlorhexidine to thoroughly clean the site.
- Volume Matters: Collect the recommended volume of blood for optimal pathogen detection.
- Multiple Sites: Drawing blood from two or more sites increases the likelihood of detecting infections accurately.
5. Pediatric and Geriatric Techniques
Special populations, such as children and older adults, require tailored approaches:
- Pediatric Patients: Use smaller needles, employ distraction techniques, and create a comforting environment.
- Geriatric Patients: Handle fragile veins with care and select veins that minimize the risk of bruising or collapsing.
Understanding patient-specific needs is critical to building trust and ensuring successful blood draws in these populations.
Conclusion
Mastering these top five phlebotomy techniques is essential for healthcare professionals to deliver accurate and safe blood collection services. From venipuncture to capillary punctures and tailored approaches for specific patient groups, each technique plays a vital role in modern healthcare. By honing these skills, phlebotomists not only contribute to diagnostic accuracy but also improve the overall patient experience.